Detailed explanation of energy storage battery parameters
Batteries are one of the most important parts of electrochemical energy storage systems. With the reduction of battery costs, the improvement of battery energy density, safety, and lifespan, energy storage has also been widely applied. This article takes you to understand several important parameters of energy storage batteries.
Battery capacity
Battery capacity is one of the important performance indicators for measuring battery performance. The capacity of a battery can be divided into rated capacity and actual capacity. Under certain conditions (discharge rate, temperature, termination voltage, etc.), the amount of electricity discharged by the battery is called rated capacity (or nominal capacity). The common units of capacity are mAh and Ah=1000mAh. Taking a 48V, 50Ah battery as an example, the capacity of the battery is 2400Wh, which is 2.4 kWh.
Battery discharge rate C
C is used to represent the rate of charge and discharge capability of the battery. Charge discharge rate=charge discharge current/rated capacity. For example, when a battery with a rated capacity of 100Ah is discharged with 50A, its discharge rate is 0.5C. 1C, 2C, 0.5C are battery discharge rates, which are a measure of the speed of discharge. The capacity used is discharged in 1 hour, which is called 1C discharge; After 2 hours of discharge, it is called 1/2=0.5C discharge. Generally, the capacity of a battery can be detected by different discharge currents. For a 24Ah battery, the 1C discharge current is 24A, and the 0.5C discharge current is 12A. The larger the discharge current. The shorter the discharge time. When it comes to the scale of an energy storage system, it is usually expressed in terms of the maximum system power/system capacity (KW/KWh). For example, the scale of an energy storage power station is 500KW/1MWh, where 500KW refers to the maximum charging and discharging power of the energy storage system, and 1MWh refers to the system capacity of the power station. If discharged at the rated power of 500KW, the capacity of the power station will be discharged in 2 hours, and the discharge rate will be 0.5C.

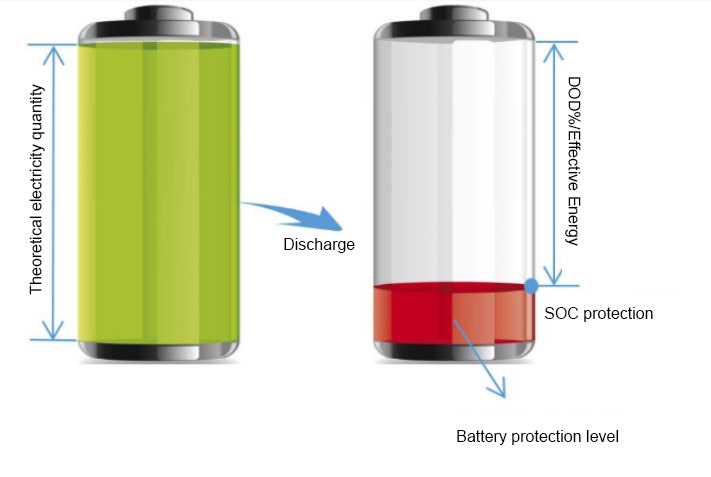
State of Charge (SOC)
The State of Charge (SOC) of a battery refers to the ratio of the remaining capacity of a battery after a period of use or long-term storage to its fully charged capacity, usually expressed as a percentage. Simply put, it is the remaining charge of the battery.

Depth of Discharge (DOD)
Depth of Discharge (DOD) is used to measure the percentage between a battery's discharge capacity and its rated capacity. The DOD depth set for the same battery is inversely proportional to the battery cycle life, with a deeper discharge depth resulting in a shorter battery cycle life. Therefore, it is important to balance the required operating time of the battery with the need to extend its cycle life.
If the change in SOC during the process of fully emptying to fully charging the battery is recorded as 0-100%, it is best to operate each battery in the range of 10% to 90% in practical applications. If the SOC is below 10%, it may cause over discharge and irreversible chemical reactions that affect the battery life.
State of Health (SOH) battery health status
State of Health (SOH) represents the ability of the current battery to store electrical energy relative to the new battery, and refers to the ratio of the current battery's full charge energy to the new battery's full charge energy. At present, the definition of SOH mainly includes several aspects such as capacity, electricity, internal resistance, cycle times, and peak power, with energy and capacity being the most widely used.
Generally, when the capacity of the battery (SOH) drops to around 70% to 80%, it can be considered to have reached the end of life (EOL). SOH is an indicator that describes the current health status of the battery, while EOL indicates that the battery has reached the end of its life and needs to be replaced. By monitoring the SOH value, the time for the battery to reach EOL can be predicted, and corresponding maintenance and management can be carried out.