Types and specifications of photovoltaic grounding
In the photovoltaic power station system, grounding design is a crucial part of electrical design, which is related to the safety of equipment and personnel in the power station. Good grounding design can ensure that the power station operates in a safe environment for a long time, reduce the frequency of faults, and improve the overall operational efficiency of the power station.
What is grounding?
Grounding refers to the connection between the neutral point of the power system and electrical equipment, the exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment, and the conductive parts outside the equipment to the earth through conductors. It can be divided into several types: working grounding, lightning protection grounding, and protective grounding.
The function of grounding?
Prevent electric shock
The impedance of the human body is closely related to the environmental conditions it is in. The more humid the environment, the lower the impedance of the human body, and the more susceptible it is to electric shock. Grounding is an effective method to prevent electric shock. After the electrical equipment is grounded through the grounding device, the potential of the electrical equipment approaches the ground potential. Due to the existence of grounding resistance, electrical equipment always has a potential to ground. The larger the grounding resistance of electrical equipment, the greater the potential to ground when a fault occurs, and the greater the danger of contact. However, if no grounding device is installed, the voltage of the faulty equipment casing will be the same as the phase to ground voltage, which is still much higher than the grounding voltage, thus increasing the risk accordingly.
Ensure the normal operation of the power system
The grounding of the power system, also known as working grounding, is generally carried out at the neutral point of a substation or substation. The grounding resistance requirement for work grounding is very small, and a grounding grid is required for large substations to ensure low and reliable grounding resistance. The purpose of working grounding is to make the potential between the neutral point of the power grid and the ground close to zero. Low voltage distribution systems cannot avoid phase line collision with the shell or ground after phase line breakage. If the neutral point is insulated from the ground, it will cause the ground voltage of the other two phases to rise to three times the phase voltage, which may result in the burning of electrical equipment with a working voltage of 220. For systems with neutral grounding, even if one phase is short circuited to ground, the other two phases can still approach the phase voltage, so electrical equipment connected to the other two phases will not be damaged. In addition, it can prevent system oscillation, as long as the insulation level of electrical equipment and lines is considered according to the phase voltage.
Prevent lightning strikes and static electricity hazards
When lightning strikes, in addition to direct lightning, induction lightning is also produced, which is divided into static and electromagnetic induction lightning. The most important method among all lightning protection measures is grounding.
What are the types of grounding?
Lightning protection grounding, working grounding, protective grounding, shielding grounding, anti-static grounding, etc.
Lightning protection grounding
Lightning protection grounding is a grounding system used to prevent damage caused by lightning strikes (direct strikes, induction, or line introduction). As a part of lightning protection measures, lightning grounding is used to introduce lightning current into the ground. The lightning protection of buildings and electrical equipment is mainly achieved by connecting one end of lightning arresters (including lightning rods, lightning strips, lightning nets, and lightning suppression devices) to the protected equipment and the other end to a grounding device. When a direct lightning strike occurs, the lightning arrester directs the lightning towards itself, and the lightning current enters the earth through its down conductor and grounding device. In addition, due to the electrostatic induction side effect caused by lightning, in order to prevent indirect damage such as building fires or electric shocks, it is usually necessary to ground the metal equipment, metal pipelines, and steel structures inside the building.

DC work grounding
Connect a point in the power system directly or through special equipment to the earth as a metal connection. Working grounding mainly refers to the grounding of the neutral point or neutral line (N line) of the transformer. The N wire must be insulated with copper core. There are auxiliary equipotential terminal blocks in power distribution, which are generally located inside the cabinet. It must be noted that the wiring terminal cannot be exposed; Cannot be mixed with other grounding systems, such as DC grounding, shielding grounding, anti-static grounding, etc; It cannot be connected to the PE line either.
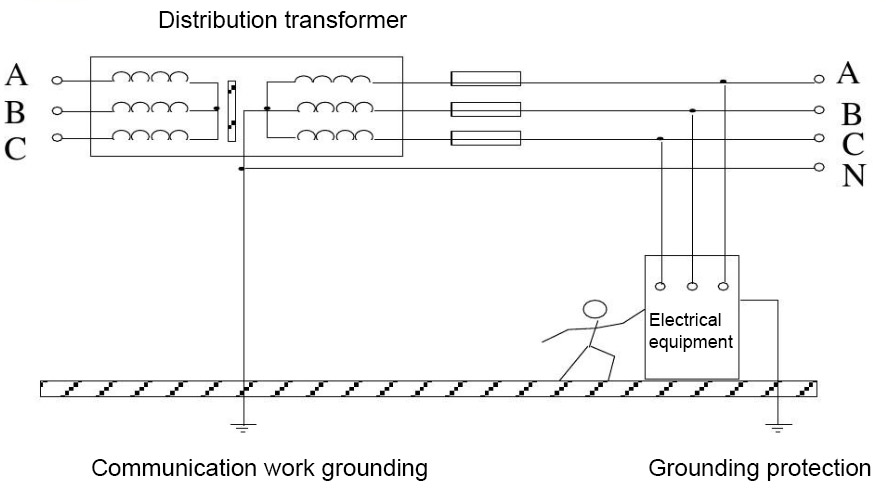
Safety protection grounding
Safety protection grounding refers to making a good metal connection between the non electrified metal parts of electrical equipment and the grounding body. In photovoltaic power plants, there are mainly several requirements for safety protection grounding, including inverters, components, and distribution boxes.
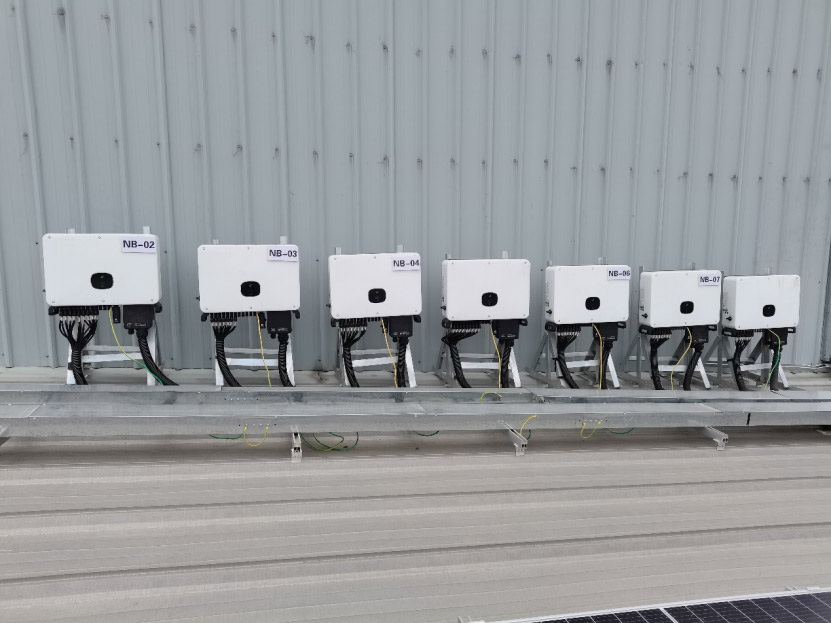

Inverter casing grounding
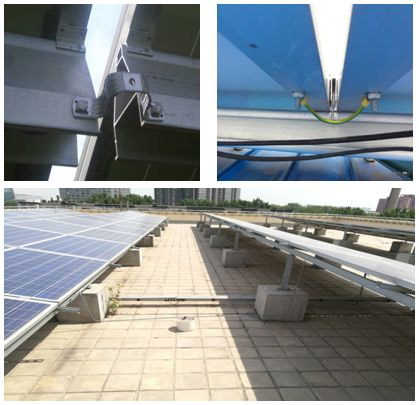

Grounding of photovoltaic modules
Shielding grounding
In order to prevent external electromagnetic interference, the grounding of the electronic device casing and the shielding wires or metal pipes inside and outside the device is called shielding grounding. This grounding method is commonly used in photovoltaic power plants for the shielding layer grounding of RS485 communication lines. It can effectively prevent electromagnetic interference in communication when multiple inverters are communicating via 485 serial communication.
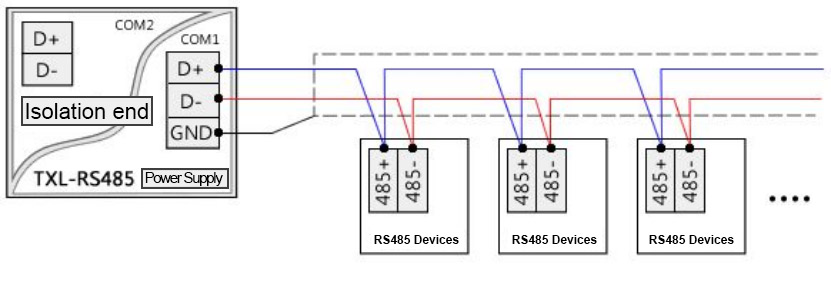
485 communication line shielding layer grounding
Anti static grounding
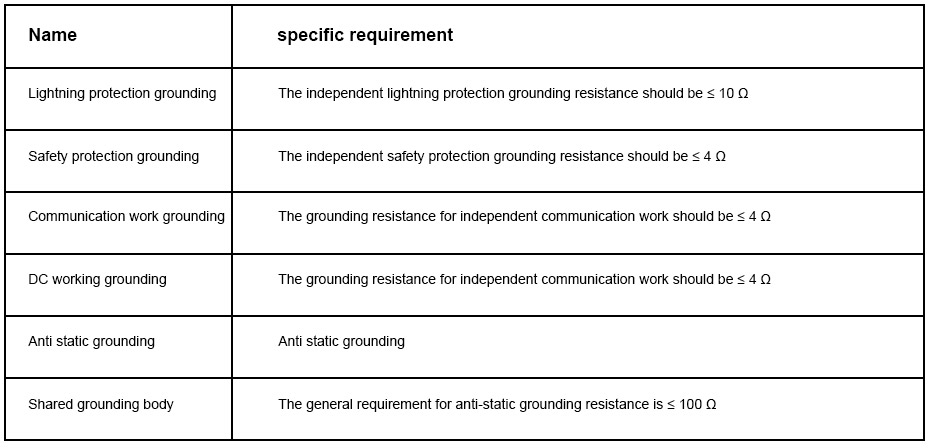
For some special inverter installation environments, such as those installed in dry computer rooms, the grounding carried out to prevent the interference of electrostatic inverters generated in the dry environment of the computer room is called anti-static grounding. The anti-static grounding device can be shared with the safety grounding device of the inverter. The standard grounding resistance specification requirements are shown in the following table:
Wrong grounding case:
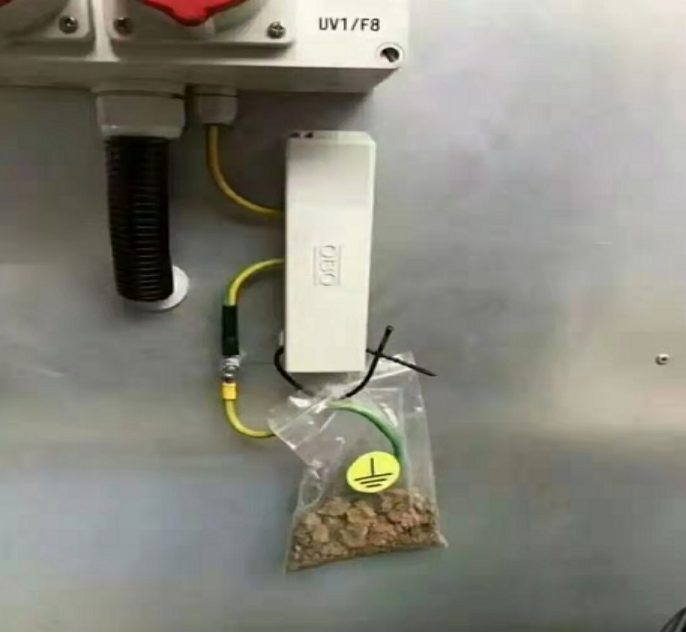

As a long-term operating system, photovoltaic power plants need to be properly grounded during design and construction to reduce unnecessary maintenance and ensure long-term stable, safe, and efficient operation of the system.